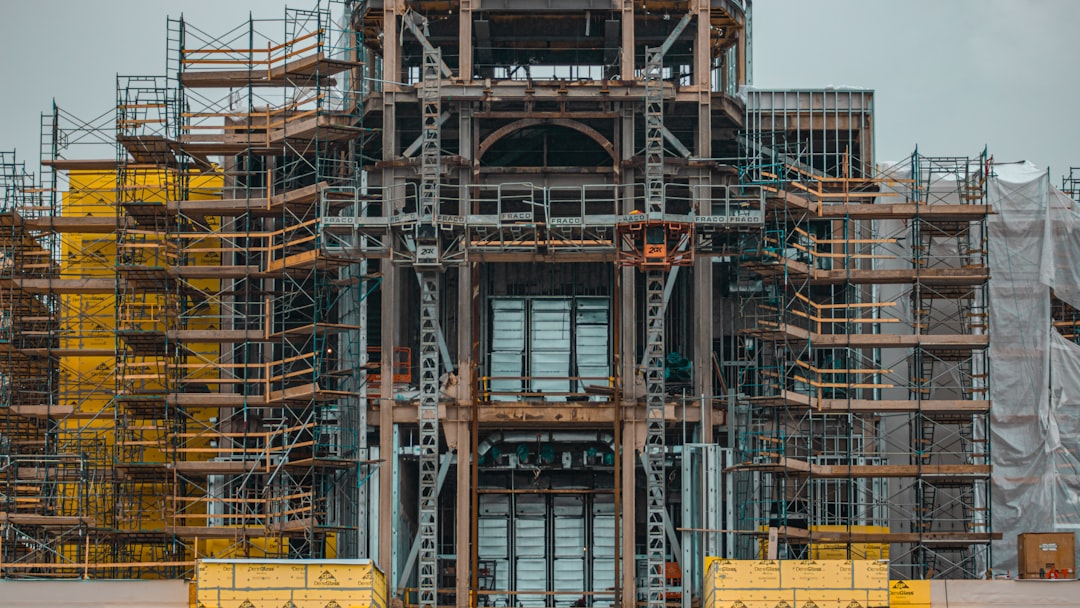
Scaffolding is an indispensable part of modern construction, providing temporary work platforms for workers to safely access various heights. At the heart of most scaffolding systems lie scaffolding pipes, the robust and versatile components that form the structural backbone of these essential platforms. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted world of scaffolding pipes, delving into their types, applications, safety considerations, regulations, and future trends.
Types of Scaffolding Pipes Used in Construction
Scaffolding pipes are predominantly made from steel, chosen for its strength, durability, and relative affordability. However, different grades and types exist, each suited to specific needs and applications. Common types include:
- Black Steel Pipes: These are the most common and economical option. They offer good strength but are susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated. Regular maintenance, including painting or galvanizing, is crucial.
- Galvanized Steel Pipes: These pipes undergo a process of galvanization, coating them in a protective layer of zinc. This significantly enhances their resistance to corrosion and extends their lifespan, making them a worthwhile investment despite a slightly higher initial cost.
- Aluminum Scaffolding Pipes: Lighter than steel, aluminum pipes are easier to handle and maneuver, particularly advantageous in projects with limited access or weight restrictions. However, they are generally less strong than steel and more expensive.
- Stainless Steel Pipes: Offering superior corrosion resistance and strength, stainless steel pipes are ideal for environments with exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme weather conditions. However, their high cost limits their use to specialized projects.
The diameter and wall thickness of the pipes also vary, influencing their load-bearing capacity and overall stability. Choosing the appropriate type and size is crucial for ensuring worker safety and structural integrity.
Applications of Scaffolding Pipes Across Diverse Construction Projects
The versatility of scaffolding pipes makes them applicable across a vast range of construction projects, from small residential renovations to large-scale industrial complexes. Some common applications include:
- Exterior Wall Construction and Repair: Scaffolding provides safe access for bricklayers, painters, and other tradespeople working on exterior walls.
- Roofing and Gutter Work: Scaffolding allows safe access to rooftops for roofing repairs, installations, and gutter maintenance.
- Bridge Construction and Maintenance: Large-scale scaffolding systems are frequently employed in bridge construction and repair projects, providing support for workers and equipment at significant heights.
- Industrial Plant Maintenance: Scaffolding provides safe access to elevated equipment and machinery for inspection, maintenance, and repair in industrial settings.
- High-Rise Building Construction: Complex scaffolding systems are essential for the construction of high-rise buildings, providing access to every level during the construction process.
The specific configuration and design of the scaffolding system will vary depending on the project’s unique requirements and the height and complexity of the structure.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices for Scaffolding Pipe Usage
Safety is paramount when working at heights. Strict adherence to safety regulations and best practices is crucial when using scaffolding pipes. These include:
- Regular Inspections: Thorough inspections of the scaffolding system should be conducted before, during, and after use to identify any potential hazards or damage.
- Proper Erection and Dismantling: Scaffolding should be erected and dismantled by trained and competent personnel following established safety procedures.
- Load Capacity Limits: The load capacity of the scaffolding system should never be exceeded. Proper calculations and weight distribution are essential.
- Use of Safety Equipment: Workers should always use appropriate safety equipment, including harnesses, safety nets, and fall protection systems.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: All scaffolding work must comply with relevant local, regional, and national safety regulations.
Negligence in safety procedures can lead to serious accidents and injuries. Prioritizing safety is not just a moral obligation but a legal requirement.
Maintaining and Extending the Lifespan of Scaffolding Pipes
Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of scaffolding pipes and minimizes the risk of accidents. This includes:
- Regular Cleaning: Removing dirt, debris, and corrosive substances prevents damage and extends the life of the pipes.
- Corrosion Protection: Regular painting or coating with anti-corrosion agents protects steel pipes from rust and degradation.
- Damage Inspection and Repair: Regularly inspect pipes for dents, cracks, or other damage. Damaged pipes should be repaired or replaced immediately.
- Proper Storage: When not in use, scaffolding pipes should be stored in a dry, protected environment to prevent corrosion and damage.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Establish a regular maintenance schedule to ensure that all components are inspected and maintained according to industry best practices.
Proactive maintenance not only ensures worker safety but also reduces the long-term costs associated with replacing damaged or corroded scaffolding pipes.
Future Trends in Scaffolding Pipe Technology and Usage
The scaffolding industry is constantly evolving, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Some future trends include:
- Lightweight Materials: The use of advanced composite materials and lighter alloys is expected to reduce the weight and improve the maneuverability of scaffolding systems.
- Smart Scaffolding Systems: Integration of sensors and IoT technology could monitor the structural integrity of scaffolding in real-time, providing early warnings of potential problems.
- Modular and Pre-fabricated Systems: Pre-fabricated and modular scaffolding systems offer faster erection and dismantling times, improving efficiency on construction sites.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Continued development of advanced safety features, such as improved fall protection systems and automated safety checks, will enhance worker safety.
- Sustainable Materials: Increased use of recycled and sustainable materials in the manufacturing of scaffolding pipes will reduce the environmental impact of construction projects.
These advancements promise to revolutionize the scaffolding industry, making it safer, more efficient, and more sustainable in the years to come.
Tags: Scaffolding pipes, construction scaffolding, scaffolding safety, steel pipes, galvanized pipes, construction safety